Bacille Calmette-Guerin (BCG) vaccination
A BCG (Bacillus Calmette–Guérin) vaccine is available for Tuberculosis (TB) but it is not part of the routine childhood immunization program, The vaccine does not prevent TB infection, BCG vaccination is most effective at preventing severe disease in infants and young children .When given to infants and young children, it minimises the risk of death, meningitis, and disseminated TB.
The vaccine which is used in Australia is the vaccine made by the India (SII) It is not formally registered for Australia – the registered vaccine has been unavailable for a few years. Vaccines made by the SII are accredited by the World Health Organisation and used in 140 countries around the globe in their national immunisation programs. This vaccination is also utilised in community clinics in Australia.
Dr Zaman Bhuiyan is an authorised prescriber of this BCG Vaccine.
Indications for BCG
BCG should be used in the following circumstances:
- newborn Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander babies in areas where tuberculosis is prevalent
- neonates and children who are likely to travel to or live in countries where tuberculosis is common
- newborn babies, if either parent has leprosy
- The kids and adults who have been in contact with tuberculosis and remain Mantoux negative three months after last contact.
BCG may also be given in the following circumstances:
- The healthcare workers who are in frequent contact with patients with tuberculosis, especially with multi-drug resistant tuberculosis
- The adults who will spend prolonged periods in countries where tuberculosis is common
- The infants who are living in households in which they may be exposed to migrants or visitors from overseas countries with high tuberculosis rates
- children under age of 16 years who are in contact with a patient suffering from tuberculosis where the infection is resistant to treatment. Also, children cannot be given prophylactic antituberculosis treatment.
Checklist before BCG vaccination
Contraindications
The vaccine should not be given to:
- Patients who are going through immunosuppressive chemotherapy or have received some treatment for malignant or non-malignant diseases in the past 6 months.
- Patients who have received or are receiving immunosuppressive therapy as a treatment of solid organ transplant. (It depends on the type of transplant and status of the patient.)
- Patients who have received immunosuppressive biological
- Patients who are receiving high-dose corticosteroids or have received them in the past 3 months.
- Adults who are taking treatment of methotrexateazathioprine non-biological oral immune modulating drugs e.g. methotrexate >25mg per week, azathioprine >3.0mg/kg/day or 6-mercaptopurine >1.5mg/kg/day
BCG vaccine is absolutely contraindicated in all HIV-positive persons
Infants born to HIV positive mothers should only be given BCG vaccination when the exclusively formula-fed infant is confirmed HIV uninfected at 12-14 weeks
- however, infants considered at low risk of HIV transmission (maternal VL <50 HIV RNA copies/mL at or after 36 weeks’ gestation) but with a high risk of tuberculosis exposure may be given BCG at birth
Pregnancy and breast-feeding
- BCG vaccination should not be given during pregnancy
- Breast-feeding is not a contraindication to BCG, however if there is any doubt as to whether an infant due to receive BCG vaccine may be immunosuppressed due to the mother’s therapy, including exposure through breastfeeding, specialist advice should be sought
Premature infants
- important that premature infants have their immunisations at the appropriate chronological age, according to the schedule
- potential risk of apnoea and the need for respiratory monitoring for 48-72h should be considered when administering to very premature infants (born <=28 weeks of gestation) and particularly for those with a previous history of respiratory immaturity
- as the benefit of vaccination is high in this group of infants, vaccination should not be withheld or delayed (3)
- if in doubt the consult specialist advice
General information:
- vaccine: live attenuated BCG bacterium
- dose: check summary of product characteristics for particular BCG vaccine to be used
Check summary of product characteristics before administration of BCG vaccine.
What to expect
Before vaccination, anyone older than 6 months will be given a tuberculin skin test (sometimes known as the Mantoux test). If the test is positive, this means that the person already has some immunity to TB and BCG vaccination is not recommended as it provides no benefit and there is a higher chance of side effects.
BCG vaccination is given by injecting a small amount of vaccine into the first layer of skin on the left upper arm.
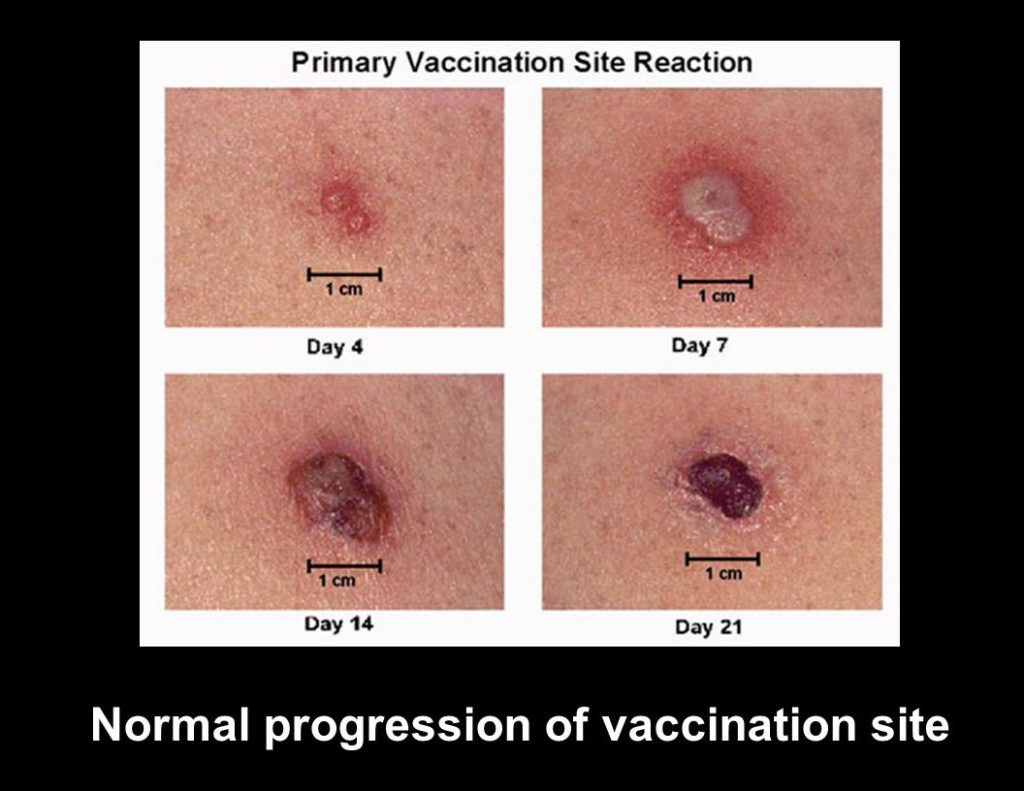
Following BCG vaccination it is normal to develop redness and/or a small lump at the injection site, followed by a small ulcer (an open sore) a few weeks later. The ulcer is usually less than one centimetre in diameter and may last from a few weeks to a few months before healing to a small flat scar.
After care instructions
• The vaccination site should be kept clean and dry. • Use clean, warm water only to clean the site when necessary. • Do not use antiseptics, creams or ointments. • Do not use sticking plaster directly over the vaccination site. If a dressing is needed, it should be a dry dressing with a strip of sticking plaster along two sides, allowing air to circulate.
Side effects
Side effects from BCG vaccination are uncommon. Temporary fever and swollen glands in the armpit or neck usually resolve without any special treatment.
The most common reactions (when they do occur) are enlarged lymph glands (about 1 in 100 vaccinations given), and abscess at the injection site (about 2 to 3 in 100)1 .
Disseminated (widespread) infection is very rare (up to 4 in 1,000,000)2 and is more likely to occur in people with weak immune systems such as people receiving treatment for cancer or other conditions or those with HIV infection.
Other rare side effects include osteitis (bone inflammation), keloid scarring and severe immediate allergic reactions.
More information visits following page
https://www.rch.org.au/immunisation/clinics/
https://www.rch.org.au/kidsinfo/fact_sheets/BCG_vaccine_for_TB/
https://www1.health.gov.au/internet/main/publishing.nsf/Content/cda-cdi3701h.htm



